Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 14 (5); September 30, 2024 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Volume 14 (5); September 30, 2024 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Research Paper
Effect of supplementation of cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) cladodes, Acacia saligna, wheat bran and cotton seed cake on feed intake, digestibility, growth and carcass characteristics of goats
Berhe G, Aregawi T and Sisay A.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(5): 274-286, 2024; pii: S222877012400032-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.32
Abstract
The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of supplementation of cactus (Opuntia ficus-indica) cladodes, Acacia saligna, wheat bran and cotton seed cake on growth, digestibility, intake and carcass characteristics of goats. A randomized complete block design was used in the experiment with 24 yearling central highland goats with an initial body weight of 15.6 - 16.1kg. The same amount of grass hay (GH) + 150 gDM/head/day wheat bran (WB) was given to all animals. The experimental diets consisted of 80 cotton seed cake (CSC) as treatment 1 (T1), 45CSC +160 cactus cladodes (CC) as T2, 45CSC+ 80 Acacia saligna (AS) as T3, and 45CSC+80CC+40AS as T4 (gram dry matter: DM, per day per goat), Data were gathered on the goats' growth, digestibility, intake, and carcass of major organs, edible and nonedible organs. The consumption of dry matter and organic matter was higher in goats fed T2 and T4 than in the T1 group. The DM, organic matter (OM) and crude protein (CP) digestibility, average daily body weight gain and feed conversion efficiency were higher in T4 and T3 goats when compared to T2 goats. Goats fed on T4 had higher hot carcass weight and dressing percentage on slaughter body weight basis than T2, T3, and T1 supplemented goats. Generally, the experimental diets improved goats’ performance in descending order (T4 > T3 >T1 >T2). Supplementation of T4 (replacement of 35 g DM of cotton seed cake per day by 40g of Acacia saligna and 80g of cactus cladodes on dry matter bases) could be recommended to improve goat performance.
Keywords: Digestion, Dry matter, Feed conversion efficiency, Goat nutrition, Protein.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Research Paper
Physical properties of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum) and tithonia (Tithonia diversifolia) shoot-based wafers with different adhesive types
Ikhlas Z, Jamarun N, Zain M, Pazla R, Yanti G, and Utami BV.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(5): 287-294, 2024; pii: S222877012400033-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.33
Abstract
Wafers (wafer-feed) are an effective processing technology and are expected to maintain the continuous availability of animal feed during the dry season. The purpose of this study was to determine the best type of adhesive on the physical quality of sugarcane tops and Tithonia based wafers. This study used the Split Split Plot Design (SSPD). The main plot as factor A was the type of adhesive, consisting of: Tapioca flour (A1), Pathi flour (A2), Gaplek flour (A3), Kariginan flour (A4), palm sugar (A5). The subplots as Factor B are temperature which consists of: 100oC (B1), 110oC (B2), and 120oC (B3), while the subplots as factor C are oven time consisting of: 10 minutes (C1), 15 minutes (C2), and 20 minutes (C3). The forage used was tabu pulp (Saccharum officinarum) and Tithonia (Tithonia diversifolia) in the ratio of 60:40. The best adhesive in making sugarcane tops and Tithonia based wafers is tapioca flour with a temperature of 120oC for 20 minutes, with physical properties such as colour, aroma, and excellent texture with a range (3.73, 3.70, and 3.63), density with a value of 5.68 g/cm3, and water binding capacity with a value of 104.22%. From the research it can be concluded that there are interactions on the physical properties of wafers (colour, aroma, and smell), density and water binding capacity.
Keywords: Binding, Physical qualities, Sugarcane shoots, Tithonia diversifolia, Wafer
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Short Communication
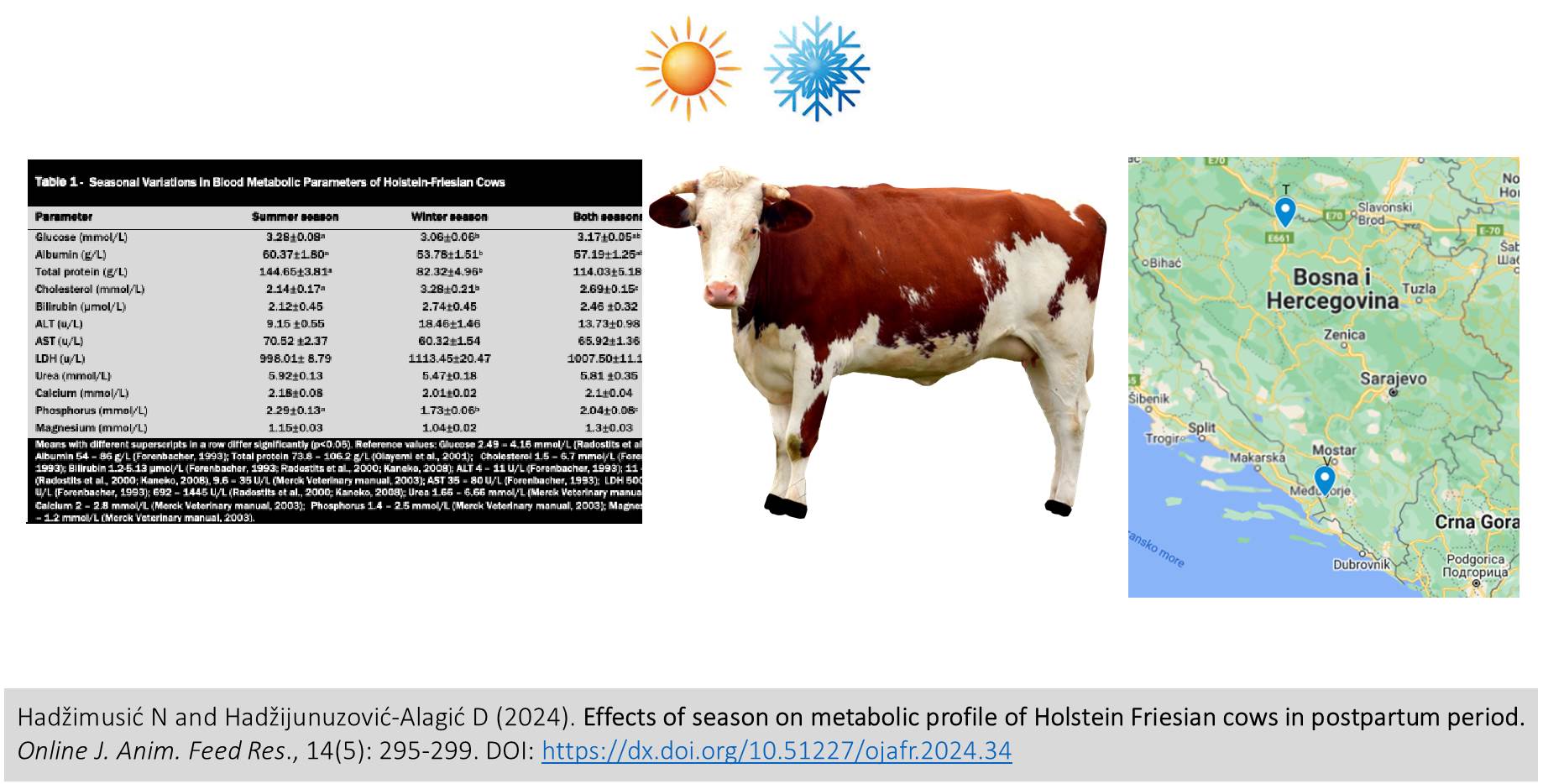
Effects of season on metabolic profile of Holstein Friesian cows in postpartum period
Hadžimusić N and Hadžijunuzović-Alagić D.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(5): 295-299, 2024; pii: S222877012400034-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.34
Abstract
The aim of the present study was to determine the metabolic profile of Holstein-Friesian cows in the postpartum period, as well as the effect of season on metabolic profile. The postpartum period is essential in the reproductive life of high yielding dairy cows because of its impact on future gravidity. This study included 60 cows up to 15 days after parturition, aged 2-8 years (the largest number of cows was between 3 and 5 years old) with no apparent clinical problems. Cows were sampled in summer season (n=30) and winter season (n=30). Parameters of metabolic profile were determined as follows: glucose, albumin, total protein, cholesterol, bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), urea, calcium, phosphorus and magnesium. Statistical differences were considered significant at the p<0.05. Present research showed that all investigated parameters were within a reference range for cattle. Impact of season sampling was determined for glucose, albumin, total protein, cholesterol and phosphorus, while bilirubin, calcium, magnesium, urea as well as activities of ALT, AST and LDH were unaffected by the season of sampling. In conclusion, metabolic status is affected by the season and examination during the postpartum period can provide valuable information of cows' health status, in order to diagnose and moreover prevent postpartum diseases.
Keywords: Cows, Climate, Health status, Metabolic profile, Postpartum period.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Research Paper
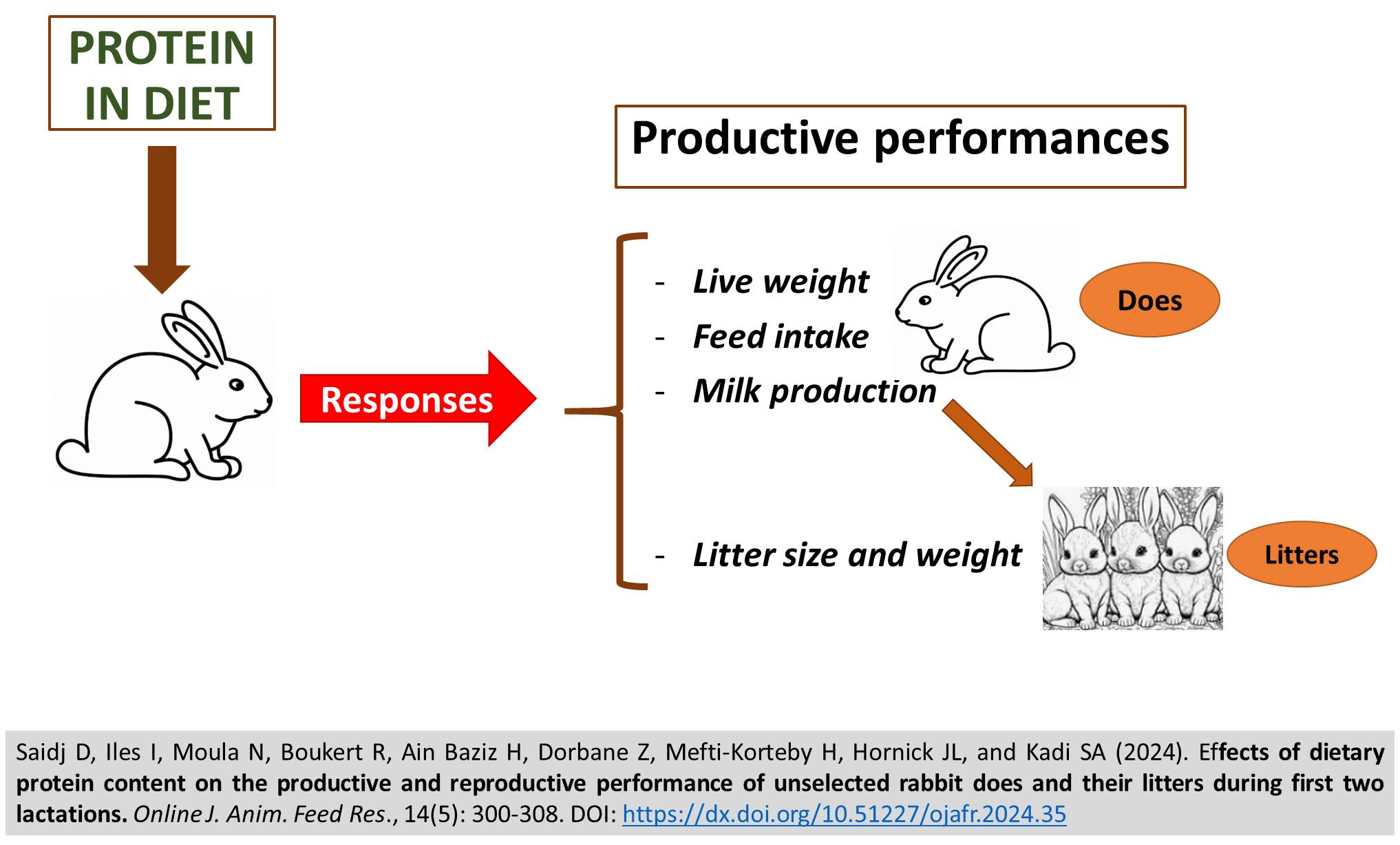
Effects of dietary protein content on the productive and reproductive performance of unselected rabbit does and their litters during first two lactations
Saidj D, Iles I, Moula N, Boukert R, Ain Baziz H, Dorbane Z, Mefti-Korteby H, Hornick JL, and Kadi SA.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(5): 300-308, 2024; pii: S222877012400035-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.35
Abstract
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the influence of different dietary protein levels on the productive performance of unselected rabbit does and their litters during their first two lactations. For this purpose, fifty-two nulliparous rabbit does, 4.5 months of age and live weight of 3115 ± 71 g, were divided into three groups (17 or 18 females per group), kept in individual cages and each group received only one of the three experimental diets. These diets were iso-energetic (10.8 MJ DE/kg), but with increasing levels of crude protein (CP): 15%, 17% and 19 % for the low (L), medium (M) or high (H) diets, respectively. Breeding was carried out by natural copulation using 6 males of 5-6 months of age and 2865±21 g initial weight, controlled semi-intensive lactation and weaning at 35 days after birth. Female body weight, feed intake, milk production, litter size and weight were monitored at birth and weekly after parturition during the first two lactations. The protein intake of the rabbits increased with the amount of protein in the diet (L vs. M: +12.2%; L vs. H: +18.8%; p < 0.001), without any effect on milk production and feed intake. Milk production was unaffected by parity. Throughout the pre-weaning period, litter size and weight and maternal mortality were unaffected by dietary protein level. Dietary protein level had no effect on live weight, birth to weaning weight gain, milk production or feed intake during the first two consecutive lactations of rabbit does.
Keywords: Feed Intake, Litter parameters, Milk production, Protein content, Unselected rabbit does, Weight gain.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Research Paper
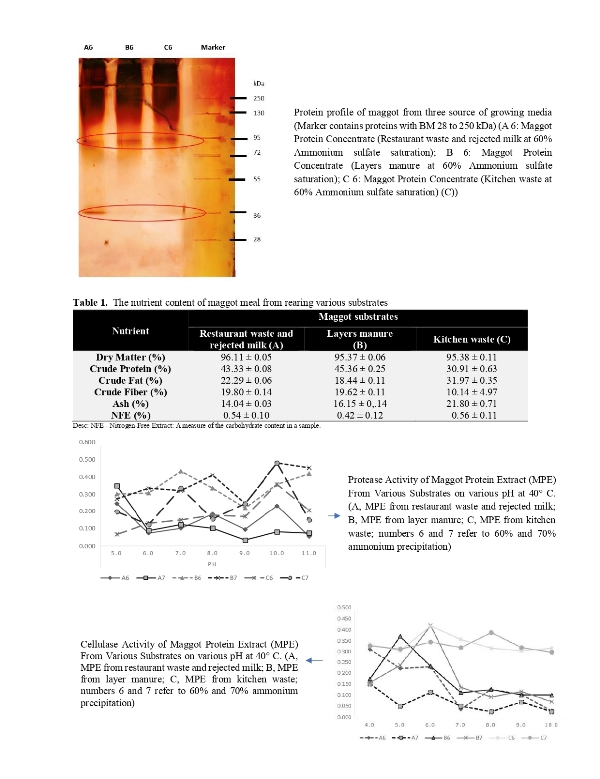
Nutrient profile, protease and cellulase activities of protein extracted from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae reared on various substrates
Widiyastuti T, Rahayu S, Suryapratama W and Suhartati FM.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(5): 309-320, 2024; pii: S222877012400036-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.36
Abstract
The Black Soldier Fly (BSF; Hermetia illucens) larvae are recognized for their ability to convert diverse organic materials into protein-rich biomass, depending on the substrate they consume. The composition of these substrates can significantly impact the nutrient profile and enzyme activities of the resulting maggot protein extract (MPE). Therefore, this exploratory research aimed to assess the nutrient content, protease, and cellulase activity of MPE obtained from BSF maggots reared on different substrates, with a specific focus on substrates A (comprising restaurant waste and rejected milk), B (layer manure), and C (kitchen waste). The results showed that maggot meal from layer manure had the highest protein content (45.36%) and the lowest fat content (18.44%). Amino acids in maggot meal contained high levels of glutamic acid, aspartic acid, alanine, valine, leucine, and isoleucine. Lauric acids were found in maggot meal from kitchen waste (33.79%), layer manure (32.18%), and restaurant waste and rejected milk (22.94%). Maggot meal from layer manure had the highest oleic acid content (15.13%). The protein concentration of MPE from various substrates ranged from 0.56 to 0.601 mg/ml (at 60% w/v ammonium sulfate saturation) and 0.555 to 0.609 mg/ml (at 70% ammonium sulfate saturation). The protease activity of MPE from layer manure substrates exhibited optimum activity and stability in neutral to alkaline pH, with activity levels of 0.748 U/mg at pH 7.0 and pH 11.0 (at 60% w/v ammonium sulfate saturation) and 0.774 units/mg at 70% w/v ammonium sulfate saturation. The highest cellulase activity was found in MPE from kitchen waste, which remained stable at pH 5.0-11.0. In general, maggots from different substrate sources exhibited distinct nutrient profiles and enzyme activities. Protein extract from maggots grown in layer manure showed the most suitable nutrient profile for use as an alternative source of protein feed and protease enzymes.
Keywords: Amino acid, Chemical profile, Enzymes, Fatty acid, Maggot.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Research Paper
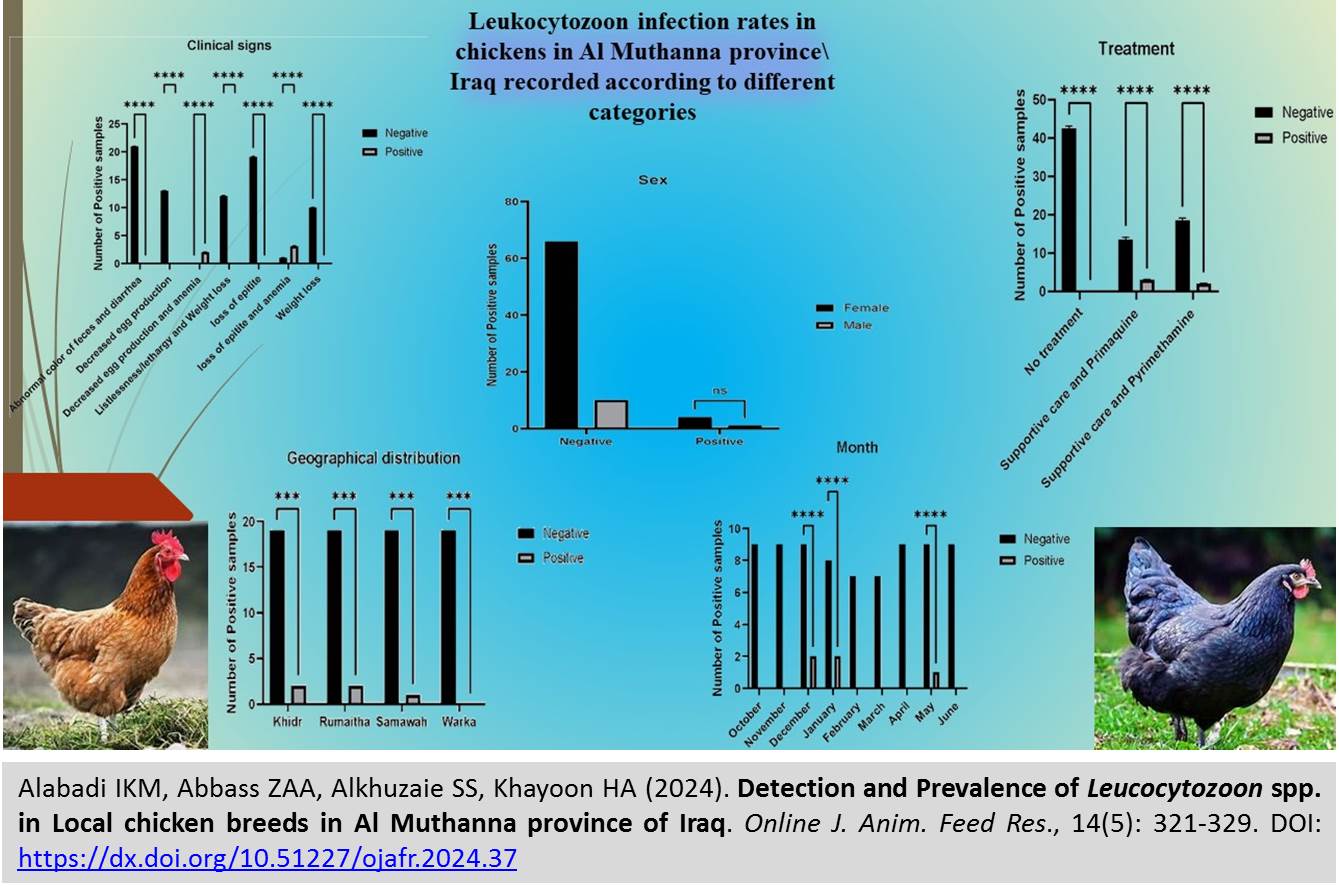
Detection and prevalence of Leucocytozoon spp. in Local chicken breeds in Al Muthanna province of Iraq
Alabadi IKM, Abbass ZAA, Alkhuzaie SS, Khayoon HA and Alsaadawi M.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(5): 321-329, 2024; pii: S222877012400037-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.37
Abstract
Leucocytozoon species are avian haemoparasites with economic impacts on poultry production. The present study investigates the presence of Leucocytozoon in chickens of Al Muthanna province, Iraq. Eighty one blood samples were collected from chickens in Samawah, Rumaitha, Warkaa, and Kidhre regions to examine the prevalence of Leucocytozoon. An infection rate of 6.1% was found among chicken breeds. The study highlighted that the main symptoms of infection were decreased egg production, anemia, and loss of appetite. Notably, infection was more prevalent in the Rumaitha, Khidr and Samawah regions, while no cases were reported in Warka. Treatment methods included primaquine and pyrimethamine alongside care to manage the condition effectively. It is important to mention that the observed prevalence rate in chickens was lower compared to studies on birds in Iraq, where an overall blood parasite prevalence of 15% was documented. This difference could be attributed to factors like habitat variations, vector presence, or differing susceptibility among bird species. Our suggestion for future work can be the application of new programs for diagnosing and controlling parasites in chickens.
Keywords: Al-Muthana region, Avian health, Flocks, Hemiparasite, Leucocytozoon spp.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Research Paper
The health and economic dimensions of honey production in Imo state, Nigeria
Nwaiwu IUO, Kadiri FA, Osuji MN, Ukoha II, Anyiam KH, Anyanwu UG, Nwosu FO, Oshaji IO, Enoch OC, Bala MB, Isaiah GI, Obasi AC, Madu JA, Nwachukwu EU, and Nnorom EI.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(5): 330-338, 2024; pii: S222877012400038-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.38
Abstract
A study was conducted on honey production in Imo state of Nigeria, with a focus on the health and economic dimensions of the industry. The research was carried out using a multi-stage sampling procedure, and a sample size of 80 honey-producer respondents was selected. Data was collected through a well-structured questionnaire and analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics. The study found that honey producers in the area had a mean age of 51 years, 11 years of education, 21 years of farming/bee-keeping experience, and a household size of 6 persons. The average annual household income was €709.10, with a farm size/number of hives kept of 72 hives per farmer and a quantity of honey produced per annum of 145 litres. The cost and returns analysis showed that the cost of production of honey per litre and profit per litre were €0.40 and €2.40, respectively. The study also determined the nutritional uses and health benefits of honey (e.g. healing wounds, treating ulcers, controlling sore throats and colds, boosting immunity, and as an antibacterial agent). Several factors, including uncontrolled bush burning, bee forage shortage, deforestation, theft of beehives, colony absconding, and poor agricultural practices which strongly constrain honey production has been observed. It is concluded that honey production is a very profitable venture with numerous uses and health benefits and venturing youths into honey production as a source of livelihood should be encouraged, and extension education should be tailored to technologies in beekeeping and the identification of genuine honey to minimize the success of adulteration, among others.
Keywords: Economic, Forage shortage, beekeeping, Honey, Health Benefits, Natural products
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Research Paper
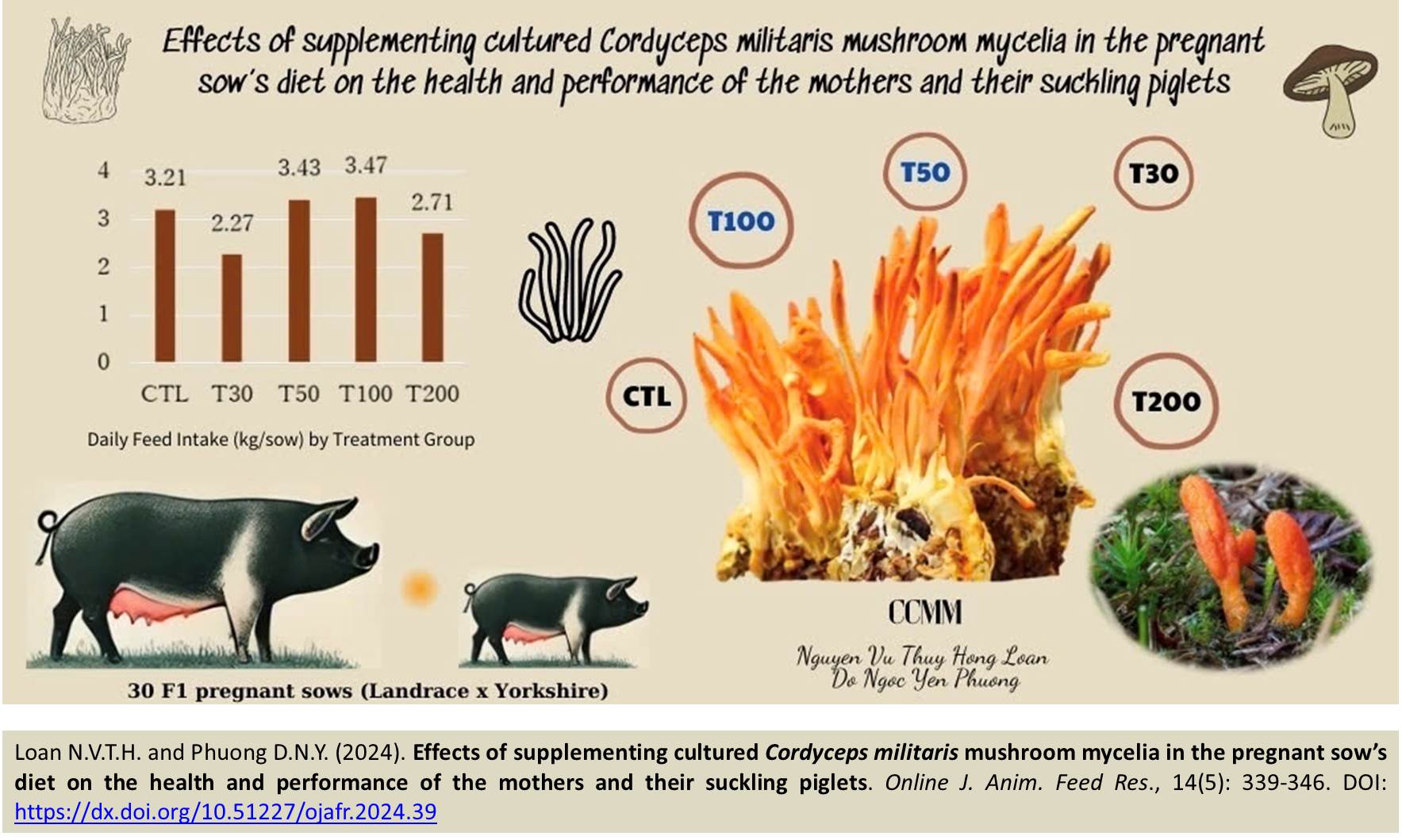
Effects of supplementing cultured Cordyceps militaris mushroom mycelia in the pregnant sow’s diet on the health and performance of the mothers and their suckling piglets
Loan NVTH and Phuong DNY.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(5): 339-346, 2024; pii: S222877012400039-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.39
Abstract
Present study aimed to evaluate the effects of supplementing cultured Cordyceps mushroom mycelia (CMM) in the diets of pregnant sows on the productivity of the mothers and their suckling piglets during their first week of age. A total of 30 pregnant F1 (Landrace x Yorkshire) sows were randomly allocated to 5 dietary treatments with 6 replicates each: Control (sows fed the basal diet), and T30, T50, T100, and T200, where sows were fed the basal diet supplemented with 30, 50, 100, and 200 g of dried CMM, respectively. The animals were individually housed and fed twice daily. The performance and health status of the sows and their piglets were recorded accordingly. The results showed that the inclusion of CMM in the diets of pregnant and lactating sows affected the performance and health status of both the mothers and their piglets. For the piglets, the total number of piglets born and alive was higher in the T50, T100, and T200 groups compared to the control and T30 groups, but there was no effect on the survival rate at 7 days old. Daily gains per piglet were higher in the T30, T50, and T100 groups compared to T200 (P<0.05). For the sows, daily feed intake was lower in the T30 group compared to the other treatments (P<0.05). The values of gross energy in the milk produced by the sows were higher in the control, T30, T50, and T100 groups compared to T200 (P<0.05). Both the piglets and the sows on diets supplemented with CMM experienced fewer health problems than those on the Control diet (P<0.05). In conclusion, the supplementation of 50 and 100 g of CMM per day in the diets of pregnant and lactating sows improved litter size and health status but did not affect the performance of either the mothers or their piglets.
Keywords: Cordyceps mushroom mycelia, Health status, Pregnant sows, Suckling piglets, Weight gain.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).![]()
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|