Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 14 (3); May 25, 2024 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Volume 14 (3); May 25, 2024 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
The polymorphism of leptin and thyroglobulin genes in Lai Sind and Lai Brahman cattle
Chau HLQ, Tra TTT, Huong DT, Hang LTT, Dung DV.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(3): 165-170, 2024; pii: S222877012400020-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.20
Abstract
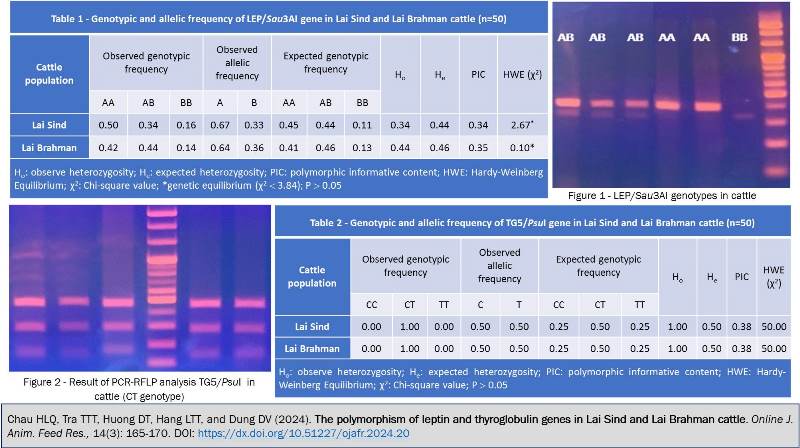
The aim of this study was to investigate the single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) present in intron 2 region of leptin (LEP) and 5’ untranslated region of thyroglobulin (TG5) genes in Lai Sind and Lai Brahman cattle populations raised in the Central Vietnam. For each cattle group, fifty hair root samples were collected and extracted genomic DNA. The LEP/Sau3AI and TG5/PsuI gene polymorphisms were analyzed using PCR-RFLP technique. The results showed that the SNPs of LEP/Sau3AI and TG5/PsuI were found in the both cattle groups. Three LEP/Sau3AI genotypes were detected, including LEPAA, LEPAB and LEPBB. All of investigated cattle carried TG5CT genotype. The Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium was reached in the both cattle populations for LEP/Sau3AI, but not for TG5/PsuI. The polymorphisms at these two loci were moderate in the both cattle populations. It can be concluded that the SNPs LEP/Sau3AI and TG5/PsuI can be used as genetic markers for molecular selection in these cattle groups. A selection program is needed to increase the frequency of TG5T allele in Lai Sind and Lai Brahman cattle groups to improve beef marbling score.
Keywords: Cattle, Lai Brahman, Lai Sind, Leptin gene, Polymorphism, Thyroglobulin gene.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Nutritional and chemical composition of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) accessions in mid-altitude of Soddo and Abeshgie Woredas of Ethiopia
Abebe DG, Cherkos SD, Ejeta TT, Dejene M, Shignato TK and Geletu AS.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(3): 171-184, 2024; pii: S222877012400021-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.21
Abstract
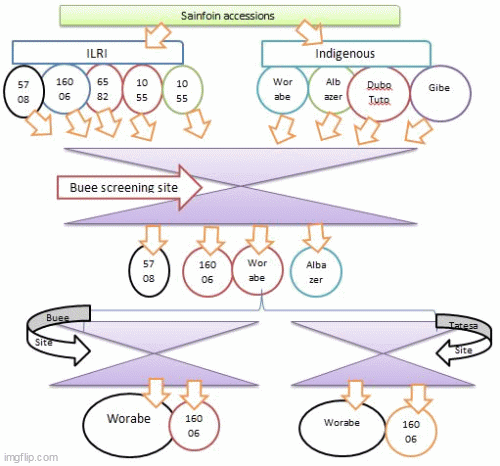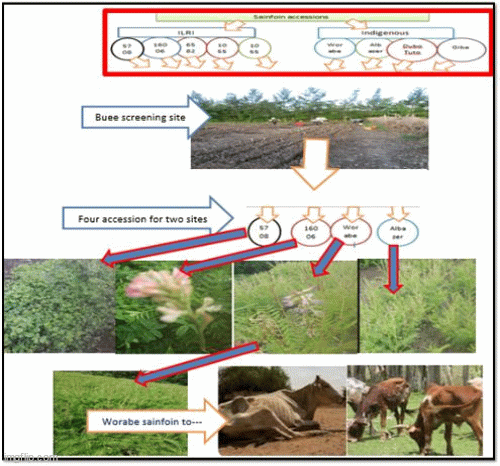
Sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) is a perennial herbaceous leguminous forage crop with a high content of crude protein, palatability, nutritive value and non-bloating. It can be offered in the form of green forage, grazing pasture, hay, or silage. To mitigate the dry season feed shortage, the agronomic performance and chemical composition of sainfoin (Onobrychis viciifolia) accessions were studied in the mid-altitude of Soddo and Abeshgie Woredas of Garage Zone of Ethiopia. For the screening, five International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) accessions (No 5708, 16006, 6582, 10558, and 10556) and four wild sainfoin accessions were collected from Worabe, Albazer, Meskan Dubo Tuto and Gibie river basin with morphological variation. They were subjected to initial screening followed by field trials for a period of fifteen months per session. Among the twenty-nine agronomic parameters (for screening purpose), based on the dendrogram results, fifteen data points were used for location wise (Buee and Tatesa) evaluation purposes. The results indicated that, with the exception leaf length, leaf width, and annual seed yield, all parameters were affected by the accession by location interaction. The highest (P<0.001) cumulative dry matter, seed yield, and crude protein (CP%) contents were recorded for Worabe sainfoin, ILRI 5708 and ILRI 16006, respectively. Lower (P<0.05) condensed tannin (CT) was recorded in ILRI 5708, Worabe’s and Albazer’s sainfoin without any significant difference. During the first 24-hour incubation period, the highest and least (P<0.001) gas were produced from ILRI 16006 and Albazer, and ILRI 5708, respectively. The highest and least (P<0.001) methane gas was recorded from ILRI 16006 and ILRI 5708 respectively. The results indicated that Worabe sainfoin was superior to the result in all evaluated parameters. So, Worabe sainfoin hay mixture with crop residues can be used to enhance the nutritional value of crop residue-based poor feed resources.
Keywords: Agronomic performance, Alternative feedstuffs, Crude protein, Dry matter yield, Sainfoin accessions.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Effects of Mango leaf powder on reproductive hormones, oxidative stress markers, toxicity indicators, growth rate and carcass characteristics of guinea pig (Cavia porcellus)
Mary Momo CM, Hervé T, Markhous Adam MT, Arthur Stella NC, Dorice AK, Adamou M, Fortune Magloire BE, Sorelle DN, Arius Baulland DN, and Ferdinand N.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(3): 185-195, 2024; pii: S222877012400022-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.22
Abstract
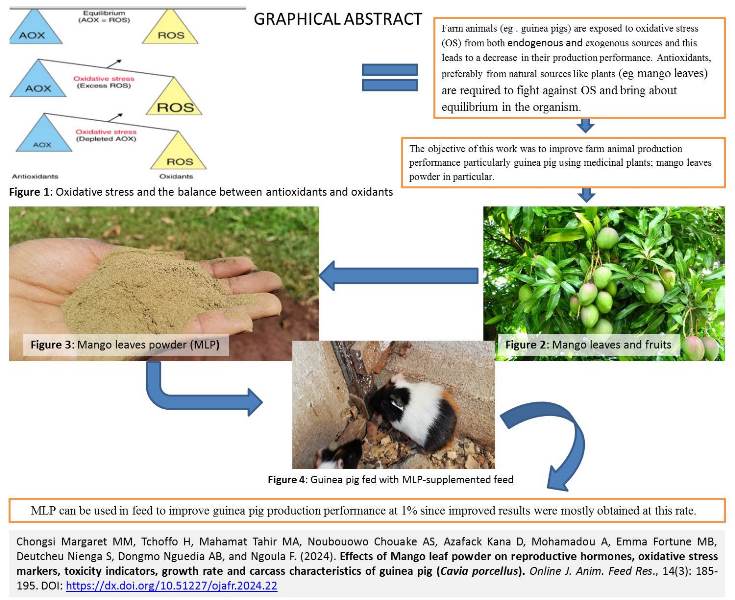
The present work aimed to evaluate the effects of Mangifera indica leaf powder (MLP) on reproductive hormones, biomarkers of oxidative stress and toxicity, growth and carcass characteristics of female Cavia porcellus. 40 female guinea pigs (Cavia porcellus L.) aged 2 months with an average weight of 257.65±11.28 g were used. These guinea pigs were weighed, then randomly divided into 4 groups of 10 animals each and subjected to the following rations: T0 (basic diet), T1, T2 and T3 (basic diet + 0.50; 0.75 and 1% MLP, respectively). For 45 days, the guinea pigs of all groups received ad libitum drinking water and the corresponding experimental rations. Reproductive hormones analyses showed a significant (P<0.05) rise in serum progesterone concentration in the highest dose of MLP-treated guinea pigs. Malondialdehyde level was lowest in guinea pigs given feed with the highest dose of MLP while superoxide dismutase and catalase activities were maximum in animals that received the highest doses of MLP. Total Peroxidase activity was greatest in animals fed with the higher MLP dose. The lowest level of cholesterol was noticed in the group that received the greatest dose of MLP. Feed consumption was higher in guinea pigs receiving 0.75% and 1% MLP. The body weight gain and average daily gain had higher values in the subjects fed with MLP feed than those of the control group. Feed efficiency values were improved in animals that that were given 0.5% and 1% MLP with regards to those fed without MLP, the length of small intestine was higher (P<0.05) in 0.75% MLP-treated animals than the other groups, while the greatest value for the density of big intestine was recorded in those that received 0.25% MLP. Based on these values (1% of diet as optimum level), MLP can be used in feed to improve animal production performance.
Keywords: Antioxidant, Average weight, Mangifera indica, Oxidative stress, Reproductive hormones.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
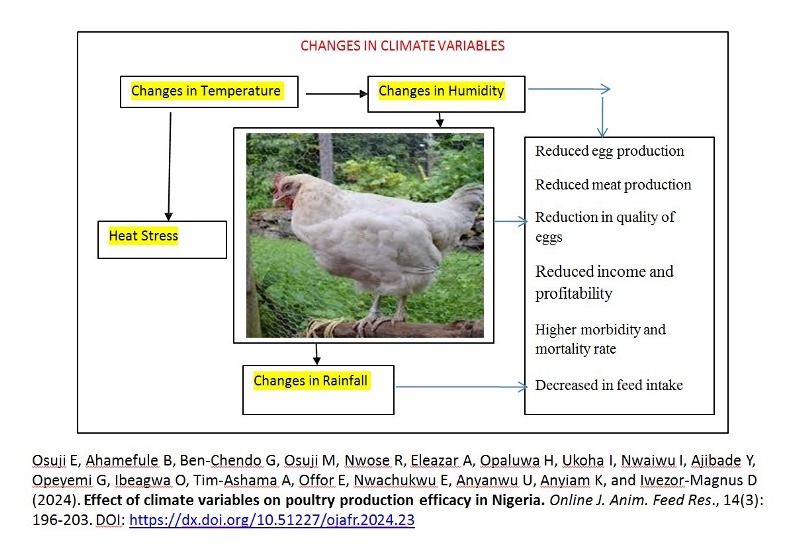
Effect of climate variables on poultry production efficacy in Nigeria
Osuji E, Ahamefule B, Ben-Chendo G, Osuji M, Nwose R, Eleazar A, Opaluwa H, Ukoha I, Nwaiwu I, Ajibade Y, Opeyemi G, Ibeagwa O, Tim-Ashama A, Offor E, Nwachukwu E, Anyanwu U, Anyiam K, and Iwezor-Magnus D.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(3): 196-203, 2024; pii: S222877012400023-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.23
Abstract
The paper examined the effect of climate variables on poultry production efficacy in Nigeria with emphasis on broilers and layers. Multi-stage sampling was used to select 401 poultry farmers who provided useful information with the aid of a questionnaire. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, and logit regression model. Result shows that free range accounted for 22.7%, battery cage 11.2%, deep litter 54.6%, and semi-free range 11.5% were notable systems of poultry rearing in the state. Heat stress 75.1%, reduced egg 99.8% and meat production 88.5%, and reduction in quality of eggs 51.9% were some of the climate change effects on poultry production. Adaptation strategies of poultry farmers include; proper housing system 100%, proper feed formulation 99.8%, right stocking density 96.8% and adequate water and feed supply 82.8%. Age, education, off-farm activities, size of poultry pen and poultry farming experience were important adaptation determinants of poultry farmers to climate change. High price of feed 100%, lack of access to credit services 77.1%, disease outbreak and parasites 100% and high cost of poultry inputs 99.5% constrained poultry farming. The study concludes that climate variable affects poultry farming. Farmers were recommended to practice climate smart poultry production to mitigate adverse effects.
Keywords: Climate Change, Farm Efficacy, Poultry Farmers, Poultry Production
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
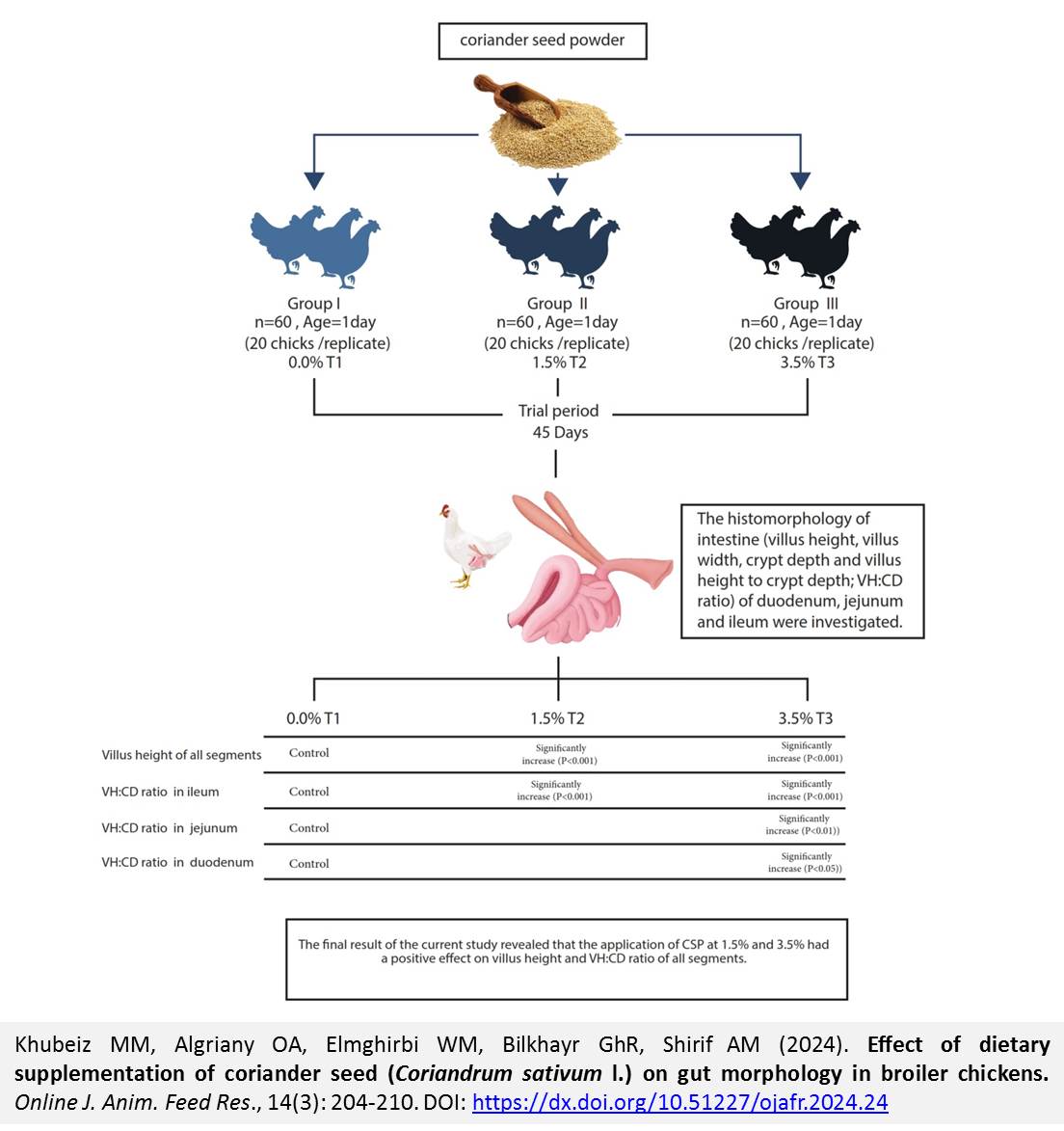
Effect of dietary supplementation of coriander seed (Coriandrum sativum l.) On gut morphology in broiler chickens
Khubeiz MM, Algriany OA, Elmghirbi WM, Bilkhayr GhR, Shirif AM.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(3): 204-210, 2024; pii: S222877012400024-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.24
Abstract
Several herbal plants have demonstrated remarkable efficacy in modulating the morphology of the gut, leading to improved nutrients absorption, enhanced growth, and reduced susceptibility to diseases. Aim of this study was to investigate the effects of different levels of coriander seed powder (CSP; 0% as T1, 1.5% as T2 and 3.5% as T3) in modulating of broiler chickens gut morphology. A total of 180 one-day-old broiler chicks were randomly allocated into 3 treatment groups 60 chick/group in 3 replicates. The trial was designed according to a completely randomized design for 45 days. The histomorphology of duodenum, jejunum and ileum [villus height (VH), villus width, crypt depth (CD) and villus height to crypt depth; VH:CD ratio] were investigated. The result showed a significant increase (P<0.01) of villus height in two treatments (1.5% and 3.5%) as compared to control in all segments. Moreover, the significant increase (P<0.01) on VH:CD ratio is observed between treatments as compared to control in ileum and dietary use of 3.5% CSP had significant effects on the jejunum and duodenum as compared to the control group. In conclusion, the application of CSP at 1.5% and 3.5% had a positive effect on villus height and VH:CD ratio of all segments. However, further research is required to understand the precise mechanisms underlying medicine plant effects as well as what the ideal percentage for each plant will be added for a best positive effect on performance.
Keywords: Broiler chicken, Coriander Sativum, Gastrointestinal functions, Gut Morphology Herbal additives.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
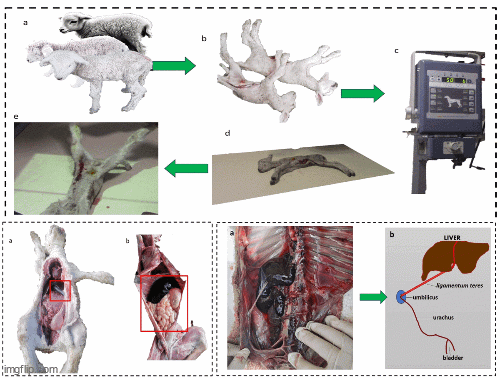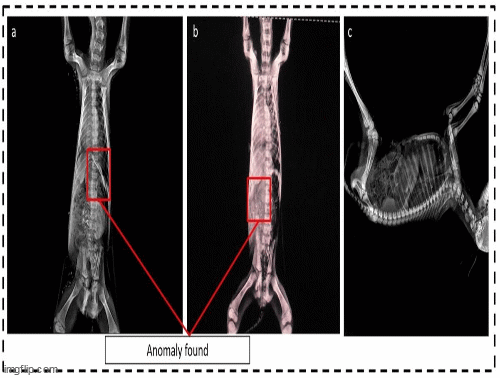
Urachus anomaly in sheep: Incidence and considerations presented in neonatal lambs in the Peru
Carhuas JN, Napoleon MS, Villar FA, Garcia-Olarte E, Eulogio CQ, Mauricio-Ramos Y, and Payano IU.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 14(3): 211-217, 2024; pii: S222877012400025-14
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2024.25
Abstract
Over the years, an anomaly has been observed in newborn lambs, manifesting itself as a curvature in their posture and a slight dampness in the navel, known by the locals as "pupote". For this reason, the present study was carried out to document and present for the first time to the scientific community an anomaly of the urachus in sheep and its incidence. In the sampling process, five lambs who died of starvation were selected. The specimens were transported to the Animal Health Laboratory of the Faculty of Zootechnics of the National University of Central Peru. Radiographic analyses were carried out there. Then the incidence was found in the collected records. The incidence of the anomaly is an average of 0.825±0.09%. This case highlights the persistence of urachus in newborn lambs, evidenced by the identification of a ligament that establishes a connection between the umbilicus and the liver. Specifically, the ligament identified in the described anomalies corresponds to the ligamentum teres.
Keywords: Congenital disease, Ligament of the liver, Pupote, Sheep breeding, Urachus.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus] [Crossref Metadata] [Export from ePrints]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).![]()
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|