Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
![]() Volume 11 (1); January 25, 2021 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Volume 11 (1); January 25, 2021 [Booklet] [EndNote XML for Agris]
Toxicity of auto-detoxified Jatropha curcas Linnaeus, 1753 kernel cake mixtures with bovine blood (ADMJKC/bb) using brine shrimp Artemia salina Linnaeus, 1758
Ewane D, Oben BO, Ndamukong KJN, Etchu KA, Ehabe EE, Chah JM, Chah KF and Mbu Oben P.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 11(1): 01-07, 2021; pii: S222877012100001-11
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2021.1
Abstract
In present study, brine shrimp (Artemia salina L.) was used to determine the toxicity of auto-detoxified Jatropha kernel cake (JKC) mixed with bovine blood (ADMJKC/bb). The powdered-JKC was mixed with bovine blood (bb) at three ratios (1:1=X, 2:1=Y and 3:1=Z of JKC: bb) and the resultant mixtures processed using four protocols: Heated, Spread Dry = 1, Unheated Spread Dry = 2, Heated Spread Remoisten to 66% dry matter (DM) = 3 and Unheated Spread Remoistened to 66% DM = 4). The resultant 12 treatment combinations (X1, X2, X3, X4, Y1, Y2, Y3, Y4, Z1, Z2, Z3 and Z4) were placed in a Solar J. curcas auto-detoxification apparatus from where samples were retrieved periodically and evaluated for detoxification using the brine shrimp lethality test. There were no significant differences within the same ratio of mixes among the four protocols. However, there was a tendency for mean LC50 values to increase between the ratios. Specifically, Protocol 2 recorded a significant difference between X2 and Z2 treatments, having 1:1 and 3:1 JKC: bb mixes respectively. Upon ranking the level of auto-detoxification, the most detoxified treatments (Z2 with LC50=4674 and Z4 with LC50 =3692) differed significantly from the least two (X1 with LC50=1383 and X2 with LC50=1459). Addition of bovine blood to JKC increased the dynamics of JKC auto-detoxification, probably due to the presence of some innate auto-detoxifying microbial inoculum and bovine blood which boost the rapid growth, development and succession of these microbes. Thus combining JKC with bovine blood is complementary for JKC auto-detoxification, with the most detoxified ingredients (Z2, Z4 and Y3) appearing most suitable for further development and testing as feed ingredient for farm animals.
Keywords: Auto-detoxification, Bovine blood, Feedstuff, Jatropha, Shrimp.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus ID: 85101775626] [ePrint] [HTML] [ePub] [XML] [Export citation to RIS & EndNote] [How to Cite]
|
|
Effect of dietary supplementation of probiotic, phytobiotics or their combination on performance, blood indices and jejunal morphology of laying hens during post peak production
Hidayat R, Yunianto VD, Sukamto B and Sugiharto S.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 11(1): 08-12, 2021; pii: S222877012100002-11
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2021.2
Abstract
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of dietary supplementation of probiotic (Lactobacillus acidophilus), phytobiotics (bay leaves, onion peel and garlic peel) or their combination on blood parameters, morphology of digestive tract and performance of laying hens. The experiment used 144 laying hens aged 72 weeks old, and divided into 6 treatments including Ctl (basal feed as control); Pr (basal feed + 1.2 mL/day of probiotic L. acidophilus); Ph2 (basal diet + 2% phytobiotic of diet); PrPh2 (basal diet + 1.2 mL/day probiotic + 2% phytobiotic); PrPh4 (basal diet +1.2 mL/day probiotic + 4% phytobiotic) and PrPh6 (basal diet + 1.2 mL/day probiotic + 6% phytobiotic). Feed intake and egg mass were weekly recorded. One chick from each replicate was blood sampled and then slaughtered for data collection. Results showed that treatments had no effect on hemoglobin, erythrocyte and leukocyte of hens. The control hens had higher levels of cholesterol and LDL than that of PrPh2, PrPh4 and PrPh6 hens. HDL level tended to be higher in PrPh2 and PrPh4 as compared to control hens. Compared to control, the villi height of jejunum was higher in the treated hens, with PrPh4 had the highest villi height. Ileal protein digestibility tended to be higher in the treated than that in control hens. Also, there was a clear tendency that feed conversion ratio was lower in the treated hens than that of control. In conclusion, the combined use of probiotics and phytobiotics improved physiological condition, ileal histomorphology, ileal protein digestibility and feed conversion of laying hens during post peak production.
Keywords: Garlic, Herb, Laying Hen, Phytobiotic, Probiotic.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus ID: 85101840385] [ePrint] [HTML] [ePub] [XML] [Export citation to RIS & EndNote] [How to Cite]
|
|
Efforts, successes and challenges of green feed production in Ethiopia
Assefa Woldemariam G.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 11(1): 13-17, 2021; pii: S222877012100003-11
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2021.3
Abstract
Improving the feed supply and digestibility of roughage through green feed supplementation was the aim of forage production in Ethiopia. In spite of the time-consumed efforts made, the success is still low. This review summarizes efforts, challenges, good practices and indicates where the focus of future efforts should be. The efforts made in improve forage production (IFP) includes selection of forage species and development strategies, preparation of extension manual, training of stakeholders, formulation of forage seed production system, and introduction of hydroponic fodder. As a result farmers increased milk production and reduce feed cost by 20% and 40 %, respectively, and fatten ruminants in 2 to 3 cycles per year as a result of improved forage use. However, there is no management model for communal grazing land. IFP constrained by long dry period, scarcity of land, irrigation and the subsistence system of livestock production and the free grazing practice. Consequently, the communal grazing lands are devastatingly overstocked and degraded, livestock become dependent on crop residues, IFP practice remains low and livestock feed deficit is common. Therefore, it is recommended that future efforts should focus on designing communal grazing land tenure model and development package. Green forge production (GFP) should concentrate on livestock excluded areas and tree legumes to produce green feed in the dry period. GFP best practices should be expanded to the areas similar to that the practices found effective. Reduce feed deficit by improving crop production to increase the crop residue and the grain yield. The subsistence system of production should be transformed into market-oriented by introducing a technology package that reduces young stock mortality, increases fertility, calf/ lamb crop and livestock offtake rate. Technical simplicity and cost-effectiveness, of the hydroponic fodder system, should be assessed before implemented in a wider setting.
Keywords: Animal Nutrition, Forage, Grazing, Green feed, Livestock.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus ID: 85101780807] [ePrint] [HTML] [ePub] [XML] [Export citation to RIS & EndNote] [How to Cite]
|
|
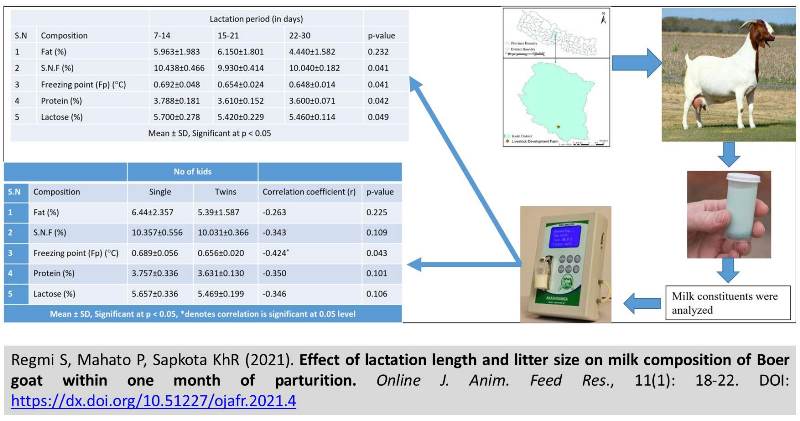
Effect of lactation length and litter size on milk composition of Boer goat within one month of parturition
Regmi S, Mahato P and Sapkota KhR.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 11(1): 18-22, 2021; pii: S222877012100004-11
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2021.4
Abstract
The aim of this study was to determine the effect of lactation length and litter size on the milk composition of Boer goats. Milk samples from 23 lactating Boer goats reared in NLBO (National Livestock Breeding Office), Pokhara, Nepal, were collected and analyzed in a laboratory present within a farm. Goats were reared under the same environment and provided with similar care and management. Lactation length showed a non-significant effect on fat content in the milk whereas all other constituents were influenced significantly. Similarly, litter size showed a significant effect on the freezing point of milk only. Litter size and all milk constituents were negatively correlated. However, Litter size and freezing point showed moderately strong correlation. Twinning did not significant influence fat, protein, lactose and solids nonfat content of goat milk. All constituents were weakly correlated to litter size however freezing point showed moderately strong correlation. Thus, more focus must be given to the nutritional management of triplets and twins to improve their growth rate compared to a single kid.
Keywords: Boer goat, Lactation length, Milk composition, Litter size, Twinning.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus ID: 85101765182] [ePrint] [HTML] [ePub] [XML] [Export citation to RIS & EndNote] [How to Cite]
|
|
Characteristics of ostrich meat in manufacturing sausage in comparison with beef
Elhashmi YH, Falih SY and Abdalmageed MEI.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 11(1): 23-27, 2021; pii: S222877012100005-11
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2021.5
Abstract
Ostrich meat has become one of the most popular meat around the world. The objectives of this study are to evaluate the quality characteristics of processed meat, compared to products made from beef. The Ostrich and beef meat was prepared and stored frozen. Sausage was processed in laboratory and analyzed for chemical composition (crude protein, moisture, fat and ash). Physical properties include Water-holding capacity (WHC), cooking loss and microbiological analysis were done. The findings of this study revealed that, chemical composition of sausage from ostrich and beef had highly significant differences in moisture, crude protein, lipids and ash among all types of products. Physical attribute of sausage revealed that, there were highly significant differences among all types of products. The microbiological in sausage observed that, the highly significant differences in E. coli, staphylococcus aurous, total coli form, yeast and mold and total viable count but was not significant differences in Pseudomonas among all types of sausage. The study recommended that ostrich meat can be used on manufacturing of meat as an alternative to beef meat in limited amount.
Keywords: Animal Product, Meat, Ostrich, Processing, Sausage.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus ID: 85101761712] [ePrint] [HTML] [ePub] [XML] [Export citation to RIS & EndNote] [How to Cite]
|
|
Biomass yield and quality of fodder from selected varieties of lablab (Lablab Purpureus L) in Nandi South Sub-County of Kenya
Wangila AJ, Gachuiri ChK, Muthomi JW and Ojiem JO.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 11(1): 28-35, 2021; pii: S222877012100006-11
DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.51227/ojafr.2021.6
Abstract
Low quality feeds is the main challenge ailing livestock production among the small-scale farmers in the tropics. Cheaper sources of alternative high quality fodder supplements are needed to improve livestock productivity. The objective of this study was to determine biomass yield and quality of fodder from selected lablab varieties. Eight lablab varieties namely, DL1002, Ngwara Nyeupe, Echo-Cream, Black-Rongai, Eldo-Kt-Cream, Eldo-Kt-Black1, Brown Rongai and Eldo-Kt-Black2 were established in three sites of Nandi south sub county, Kenya. Randomized complete block design was used at farm level with four replications per site. Data on biomass yield, chemical composition and in vitro-dry matter digestibility of the eight lablab forages was collected. Biomass yield differed significantly among the lablab varieties ranging from 5.6-12.6 t DM/ha across the three sites. Highest biomass yield was recorded for Brown Rongai (12.6 t DM/ha) and lowest with DL1002 (5.6 t DM/ha). Crude protein (CP) content varied significantly between varieties with sites ranging from 19.6-23.9 g/100g. Highest CP was recorded with Eldo-Kt-Cream and Black Rongai (23.9 g/100g and 23.7 g/100g) across the three sites. For all the varieties, Neutral detergent fibre (NDF) ranged from 44.4-48.6 g/100g, acid detergent fibre (ADF) 31.6-35.7 g/100g and acid detergent lignin (ADL) 9.0-11.9 g/100g across the three sites. Highest NDF was recorded with DL1002 (48.6 g/100g), ADF with Eldoret-Kitale-Black2 (35.9 g/100g) and acid detergent lignin with DL1002 (11.7 g/100g). In vitro dry matter digestibility (IVDMD) varied significantly between varieties and sites ranging from 67.6-75.7 g/100g between the varieties across the three sites. Eldo-Kt-cream and Black Rongai had the highest IVDMD (75.7 and 74.4 g/100g) across the three sites. Eldoret-Kitale-Cream and Black Rongai varieties had better dry matter yield, crude protein and low fibre fractions compared to the other varieties signifying their potential to be recommended as supplement to low quality fodder by small-scale farmers.
Keywords: Biomass yield, Digestibility, Feed, Fodder, Lablab.
[Full text-PDF] [Scopus ID: 85101733013] [ePrint] [HTML] [ePub] [XML] [Export citation to RIS & EndNote] [How to Cite]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive![]()
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|