Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 9 (3); May 25, 2019 [Booklet]
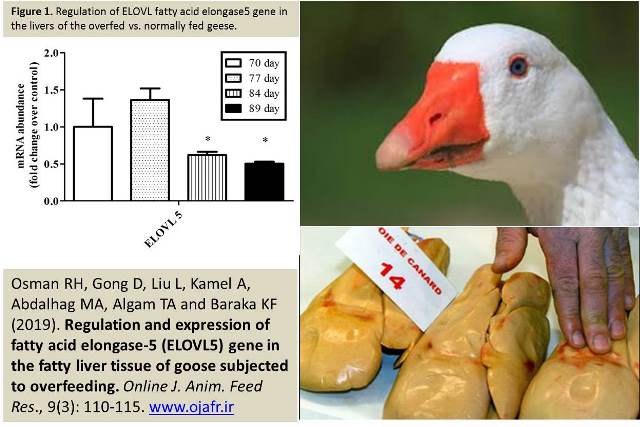
Regulation and expression of fatty acid elongase-5 (ELOVL5) gene in the fatty liver tissue of goose subjected to overfeeding.
Osman RH, Gong D, Liu L, Kamel A, Abdalhag MA, Algam TA and Baraka KF.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 9(3): 110-115, 2019; pii: S222877011900014-9
Abstract
Fatty acid elongase ELOVL plays an important role in the synthesis of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFA). The aim of this study was to investigate regulation and expression of ELOVL fatty acid elongase 5 gene in the fatty liver tissue of goose after feeding on a carbohydrate-rich diet. To understand how the Elovl5 was down-regulated in the context of fatty liver, we treated goose primary hepatocytes with fatty liver-related factors, including high levels of glucose, fatty acids and insulin. Together, the present study suggested that the reduction of Elovl5 expression is required for the development of goose fatty liver. We hypothesized that ELOVL5 are involved in goose fatty liver development. To address this, we determined the response of goose ELOVL5 gene to overfeeding and their expression in goose liver and primary hepatocytes with some related factors such as glucose, fatty acid and insulin. Expression data indicated that ELOVL5 was significantly reduced after a period of force-feeding lasting 2 weeks of overfeeding. In primary hepatocytes, gene expression was not affected by glucose and palmitate treatment while expression reduced by high level of insulin 50mM and 100mM. Also when we treated with 0.25Mm of Oleate the expression level rapidly down-regulated.
Keywords: Fatty liver, Goose, ELOVL fatty acid elongase-5, Overfeeding
[Full text-PDF]
Challenges of dairy production and marketing in urban and peri-urban areas of Amhara region, Ethiopia.
Moges N, Getu A, Guadu T, Bogale B, Mengistu A, Tesfaye Sh.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 9(3): 116-124, 2019; pii: S222877011900015-9
Abstract
Dairy production is an important component of livestock farming in Ethiopia. The huge and diverse livestock population, varied and favorable agro-ecology is good for dairy production to answer the demands for dairy products in urban and peri-urban areas. The aim of the study was to assess the challenges of dairy production and marketing in urban and peri-urban areas of Amhara region. Therefore, a total of 885 households were randomly selected for interview. In the dairy farm, the major feed resources used by the households were natural pasture (4.5%), concentrate feed (60.9%) and both pasture and concentrate feed (34.1%). According to the information stated by the respondents industrial by products (6.0%), hay (20.5%), straw and brewery by products (0.7%) were used as important feed resources, while 97% of the overall respondents stated that water available was accessible throughout the year. Whereas, the major challenges for dairy production interims of diseases in the current studied areas were mastitis (11.5%), ectoparasite infestation (10.6%), lumpy skin disease (2.7%) and foot mouth disease (1.9%). In addition, milk production and marketing system in the areas were highly challenged by disease prevalence, feed scarcity feed quality, and distant traveled to sell milk and seasonal price variation. Developmental constraints were also reported like lack of infrastructure and finance, poor education of households, seasonality of supplies and the lack of market and marketing infrastructure and facilities. On the same time reproductive problems like sterility, abortion, immature birth, retained placenta, repeat conception and dystocia with the proportion of 3.6, 23.7, 1.8, 9.9, 17.9, 9.1 and 34% respectively were reported. Therefore, feed scarcity throughout the year, disease prevalence and veterinary service problem are some of the identified challenges. So, appropriate research work, development, policy and crosscutting interventions should be taken in to account to make improve the dairy industry
Keywords: Dairy Production, Marketing, Urban, Peri Urban, Amhara, Ethiopia.
[Full text-PDF]
Assessment of prescription patterns of veterinary drugs in Gondar, north west Ethiopia.
Berihun B, Kebede E, Birhan M and Mohammed A.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 9(3): 125-133, 2019; pii: S222877011900016-9
Abstract
Veterinary drugs play an important role in the control and prevention of animal disease, but have the potential to cause harm if not used rationally. Irrational prescription of drugs is a common occurrence in veterinary clinical practice. To evaluate the prescription patterns of veterinarians and animal health workers in Gondar town of three veterinary clinics, Northwestern Ethiopia. A retrospective study was conducted using a systematic random sampling method of 1000 patient’s encounters. Data were collected from prescription and case books retained in the clinic for the last two years. Average number of drugs per encounter in these health facilities was 1.291. Generic prescribing was low at 88.40% while encounters with antibiotic prescription were high at 44.4%. About 98.20% of prescribed drugs were listed in the national veterinary drug list while 64.4% of encounters had at least one injection prescribed. The most commonly prescribed drugs were Albendazole 330(25.6%), Oxyteteracycline 243(18.8%), Ivermectin 157(12.16%), Penicillin and Streptomycin fixed combination 133(10.3%), Acaricides 108(8.3%), vitamin supplements 77(6%), and other drugs including gastrointestinal stimulants, Anti-acids, anti-inflammatory drugs, lubricants and anti-foaming agents 243(18.8%). Among a total of 1000 animal patient encounters, only 158(15.8%) prescription contain name of the prescriber, while 128(12.8%) of prescriptions have signature of the prescriber and 109(10.9%) of prescriptions contained qualification of the prescriber. The prescribing practices for antibiotic, genetic drug and injection shows deviation from the standard recommended by WHO, so it should be improved. On the other hand, polypharmacy, generic prescribing and prescribing from Ethiopian veterinary drug list were not found to be a problem in this study. Further comprehensive studies on medication error are necessary to investigate the scale of problem and their economic impact.
Keywords: Assessment, irrational drug use, Prescription, Rational Veterinary
[Full text-PDF]
The influence of dried brewery grain in broiler diets on production performance.
Kuleile N, Adoko G and Nkheche M.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 9(3): 134-138, 2019; pii: S222877011800017-9
Abstract
As a result of high feed costs in Lesotho the majority of farmers especially those producing under semi intensive are diluting commercial feeds with a non-conversional feeds such as dried brewery grain (DBG) in order to increase the quantity and to lower the costs of feeds. In most cases this practice resulted in poor broiler performance and low carcass yields because of high inclusion rates. A completely randomized study with four dietary treatments was undertaken at the National University of Lesotho farm. The aim of the study was to investigate the effect of DBG inclusion in broiler diets during growing and finishing and to determine the dilution or the inclusion rate that can maintain broiler performance and carcass yields like commercial feeds. Dietary treatments were made up of control represented by commercial feeds and three inclusion rates of DBG at 25, 50 and 75% respectively. A total of 360 day-old Ross 308 chicks were randomly assigned to four treatments replicated four times. A total of ten birds per replicate were used for carcass parameters determination. Feeds and water were provided on ad libitum basis. Light was provided for maximum of 20 hours per day. Performance data were collected on weekly basis as average feed intake, growth rate, body weight, feed conversion ratio and mortality while carcass parameters were collected at the end of finishing phase on carcass weight, dressing percentage, gizzard and intestinal weight. The feeding experiment lasted for four weeks. The dietary treatments had a significant (P<0.05) effect on average feed intake, growth rate, body weight, feed conversion ratio, carcass weight, dressing percentage, gizzard and intestinal weights whereby broilers under control and 25% DBG had similar and better performance than animals in other treatments except for gizzard and intestinal weight which were higher in 75% DBG. The higher fibre content of DBG was found to be the limiting factor in the utilization by broiler especially at inclusion rate beyond 25%. Cost benefit analysis indicated that there was a 21% reduction in feed costs when using 25% DBG in broiler diets. It was concluded that 25% DBG inclusion rate is the one giving similar production performance and carcass yield to the commercial feeds except for the visceral parts. Therefore farmers can include the DBG up to 25% in broiler feeds for optimum performance and carcass yield between growing and finishing stages and save 21% in feed costs.
Keywords: Dried brewery grain, Commercial feeds, Broiler performance, Carcass parameters, Feed costs.
[Full text-PDF]
Assessment of major reproductive disorders of dairy cows in Gondar town, north west Ethiopia.
Simeneh Y and Moges N.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 9(3): 139-145, 2019; pii: S222877011800018-9
Abstract
A cross sectional study was conducted in Gondar town from November 2016 to April 2017 with the objectives of determining the prevalence rate of major reproductive health problems of dairy cows and assessing risk factors with roles in predisposing to reproductive problems. Cross sectional questionnaire survey and regular follow-up were used to determine reproductive parameters and abnormalities. The study was carried out on a total of 316 dairy cows. From the total study animals 25% (n=79) were affected by at least with one reproductive health problem. Among the problems repeat breeder, retained fetal membrane, abortion and anestrous were mostly found with their respective prevalence of 6.96%, 6.01%, 3.48% and 2.53%. The overall prevalence of reproductive problems were significantly (P<0.05) influenced by breed, production system, age, parity, body condition and hygiene. Generally the current finding revealed that reproductive health problems commonly exist in the study area through their percentage and types vary from time to time; hence, regular reproductive health management and proper formulation of ration could be the possible solutions to alleviate the problems encountered in different production systems. From the different risk factors studied BCS and parity were significantly associated with reproductive health problems. From this study feeding, housing and health managements should be restudied and improved to reduce the incidence of reproductive problems. This study showed that reproductive disorders highly affected the reproductive performance of dairy cows. Further detailed studies on the major reproductive health disorders in the area should be carried out.
Keywords: Dairy cows, Gondar town, Reproductive health problems.
[Full text-PDF]
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive![]()
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|