Previous issue | Next issue | Archive
Volume 5 (6); November 25, 2015 [Booklet]
 Research Paper
Research Paper
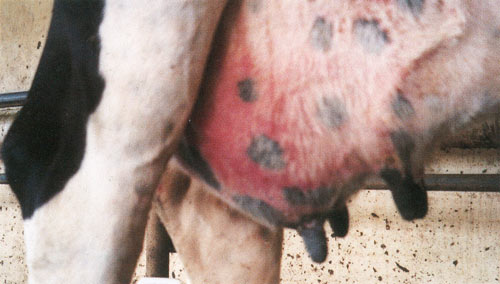
Update on bovine mastitis etiological, clinical and treatment aspects in Khartoum state, Sudan.
Mohammed Salih R.R.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 5(6): 153-159, 2015; pii: S222877011500025-5
Abstract
This study was conducted in certain area at Khartoum State determine the causative agent of bovine mastitis and the susceptibility of different isolates to different antibiotics use for treatment of bovine mastitis. The total number of dairy cows, which were examined in 34 investigated farms, equals 500. The result as follows: 55% acute mastitis, 44% chronic mastitis and 1% gangrenous mastitis. The isolated genera were as follows: 74% Bacillus spp., 24% Staphylococcus spp., 1% Corynebacterium spp. and 1% Klebsiella spp. The isolated species were as follows: 31% Bacillus coagulans, 11% B. cereus, 9% B. subtilis, 9% B. licheniformis, 4% B. circulans, 2% B. lentus, 3% B. mycoides, 3% B. amyloliquefaciens, 2% B. megaterium, 16% Staphylococcus aureus, 8% Staphylococcus hyicus, 1% Corynebacterium spp. and 1% Klebsiella spp. Lastly, the sensitivity test was applied using different antibiotics were as follows: Hundred percent of isolates were sensitive for Chloramphenicol and Ciprofloxacin, 91.6% for Gentamycin and Piperacillin/ Tazobactam, 83.3% for Pefloxacin and Tetracycline, 75% for Amikacin and Ofloxacin, 66.6% for Ceftizoxime, 33.3% for Co-Trimoxazole and Cefotaxime and 16.6% for Ampicillin/ Sulbactam. This study was depended at routine works at microbiological laboratory.
Keywords: Bovine Mastitis, Etiology, Clinical, Treatment, Khartoum, Sudan
 Research Paper
Research Paper
Effect of Different Stocking Densities on Survival Rates of Nile Tilapia Fingerlings Transported in Plastic Bags.
Adam Ibrahim AM, Yagoub Adam HM., Musa Ahmed A.M, Mirghani Yousif F.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 5(6): 160-164, 2015; pii: S222877011500026-5
Abstract
Fish farmers in Sudan obtain their seed stocks mainly not from their farms and as such rely heavily on good packing conditions covering sometimes 8–12 hours transportation time to maximize fish survival and quality the study here required main objective to identified the optimum loading for the success during transporting. closed oxygenated plastic bag which was carried three densities for each one with tow replicate for every treatment for the lower loading is 75 fingerlings /l the medium is, 100 fingerlings and last density is the larger one 140 fingerlings the duration factors was 10 hours, 11 hours and 18 hours. The fingerlings was sex reversed, their size is (5g ± 0.5). The collecting data analyze used SPSS computer software version- 16.0. Analysis result shown the factor of density in the tow treatments (75 fingerlings + 100 fingerlings) was the best according to the survivor rate depending to type of the periods parameter. 10 hour=94% and 11 hours = 92% and here was N.S otherwise the comparative between those and the density 140 was high significant. Variation between loading and durations is NS at P<0.05, so the conclusions is found the optimum loading during transporting period was 100/l/18 (hundred fish per litter in 18 hours period) according to analysis details.
Keywords: Transport, Survival Rates, Fingerlings, Nile Tilapia, Plastic Bags.
Research Paper
Isolation of Klebsiella Spp. from Gangrenous Mastitis in Cattle in Khartoum State, Sudan.
Mohammed Salih R.R, Mohamed Ahmed F.A.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 5(6): 165-168, 2015; pii: S222877011500027-5
Abstract
This study was conducted in Khartoum State to determine the causative agent of gangrenous mastitis in bovine. Hundred dairy cows were examined after collected aseptically from 41 cows suffering from mastitis. All these cows were examined by visual inspection and palpation of mammary gland and supra-mammary lymph nodes. The milk samples were examined bacteriologically. The result was as follows: 55% acute mastitis, 44% chronic mastitis and 1% gangrenous mastitis. The isolated genera were as follows: 74% Bacillus spp., 24% Staphylococcus spp., 1% Corynebacterium spp. and 1% Klebsiella spp. The isolation of Klebsiella spp. from gangrenous mastitis in Frisian cow is considered as the first of its type in Sudan.
Keywords: Bovine, Gangrenous, Mastitis, Klebsiella, Khartoum, Sudan.
 Review
Review
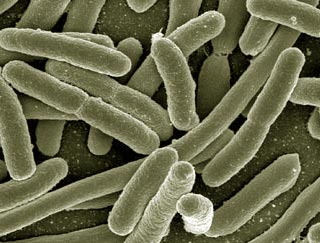
Review virulence nature of Escherichia coli in neonatal swine.
Paul N.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 5(6): 169-174, 2015; pii: S222877011500028-5
Abstract
Piglet disease due to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) are classical and associated typically with severe watery diarrhea within the first two weeks of life and occasionally some days after weaning in pigs. E.coli is a well-known and diverse organism though normally harmless commensal, but when it acquires mobile genetic elements becomes a highly pathogenic organism capable of causing a range of diseases. ETEC adhere to the small intestinal microvilli without inducing morphological lesions and produce enterotoxins acting locally on enterocytes. This leads to hyper-secretions and reduced absorption of electrolytes. The virulence attributes of ETEC are adhesions and toxins and the successful management of the disease is dependent on good understanding of these virulence factors. In pigs ETEC, the commonest adhesions are the fimbriae on the surface K88, K99, 987p, F18ab and F18ac. The enterotoxine of pigs ETEC are further classified into heat-labile (LT) and heat-stable (ST). Other subdivisions of enterotoxin E. coli are LT, STb, STa, Stx2e. The adhesive fimbriae and enterotoxins of piglet ETEC can be evaluated using plasmids. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a specific test and had been used for virulence gene detection of ETEC. In this reviews, we focus on current opinions and knowledge of the various pathogenic pathways that E.coli uses to cause disease in piglet.
Keywords: ETEC, Fimbria, Toxins, Piglets, Virulence
 Research Paper
Research Paper
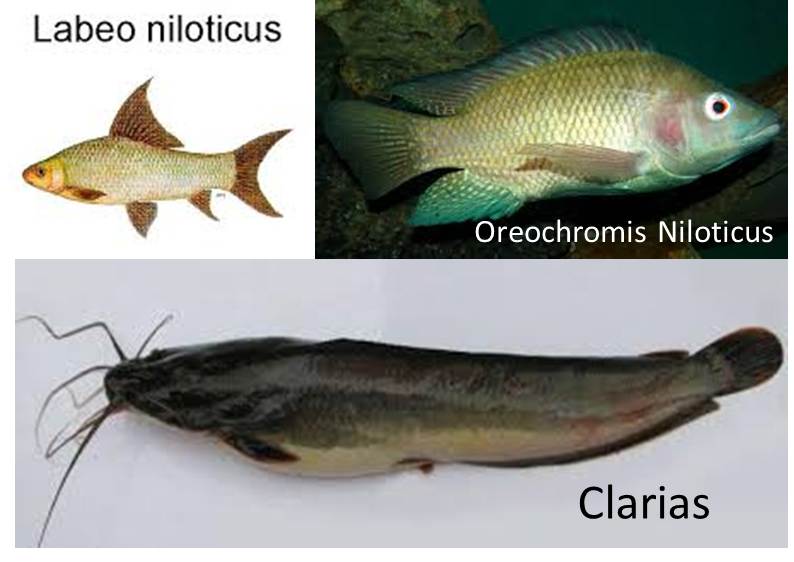
Comparative study of the body weight characteristics and effect of drying on chemical composition of three Nile fish species (Oreochromis Niloticus, Labeo Niloticus and Clarias Spp.).
Yagoub Adam H.M., Musa Ahmed AM, Adam Ibrahim A.M., Mirghani Yousif F.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 5(6): 175-180, 2015; pii: S222877011500029-5
Abstract
This study was carried out to compare the body weights of three different Nile fish species (Oreochromis niloticus, Labeo niloticus and Clarias spp.), and the impact of direct sun drying on their chemical composition.36 samples were collected (12 samples/ species). Averages of total length, standard length (cm) and gross body weight (gm) were determined and the findings were as follows: 36.5, 29.75 and 930 for Oreochromis niloticus, 49, 39.5 and 1210 for Labeo niloticus and 49, 45 and 977.5 for Clarias spp. It was noticed that clarias spp. has the highest edible meat percentage 46.75% followed by Labeo niloticus 38.82% and Oreochromis niloticus 33.39%, and there were significant differences (P < 0.05) among the three species. Chemical analysis for the samples was done to determine (protein, fat, ash and moisture contents). The results of protein contents examined were 62%, 61.5% and 61.5% for Oreochromis niloticus, Labeo niloticus and Clarias spp. respectively. Fat contents were 7.41%, 8.27% and 7.32% for Oreochromis niloticus, Labeo niloticus and Clarias spp. respectively. Moisture contents were 6.7%, 7.5% and 7.5% for Oreochromis niloticus, Labeo niloticus and Clarias spp. respectively. Ash contents were 5.90%, 6.05% and 6.85% for Oreochromis niloticus, Labeo niloticus and Clarias spp. respectively.
Keywords: Body weight, Chemical Composition, Drying, Nile fish’s spp.

Research Paper
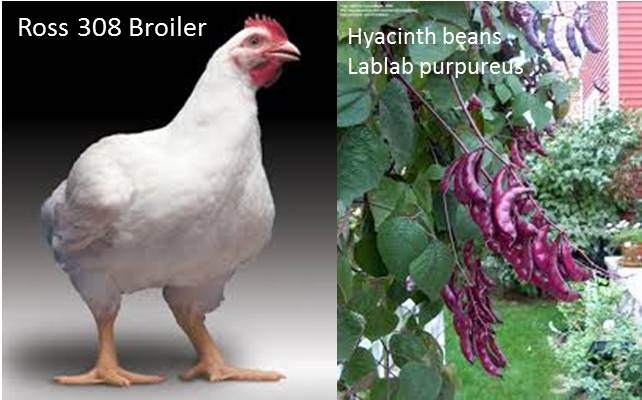
Effect of dietary Hyacinth beans (Lablab purpureus) and enzyme additives on performance of broilers.
Ragab HI, Abdel-Atti KhA, Babiker MS, Elawad SM.
Online J. Anim. Feed Res., 5(6): 181-188, 2015; pii: S222877011500030-5
Abstract
The study was conducted to assess the effect of Hyacinth beans on the performance of broilers, for a period of 47 day feeding trial. In addition to basal control (A), another treatment diets were formulated to have Hyacinth beans at 15% (B, C) without or with enzyme additives and 20% (D, E) without or with enzyme additives. A total of 150 unsexed Ross 308 chicks were randomly distributed to 5 dietary treatments, with 5 replicates (6 birds per rep) Feed and water were offered ad- libitum. Results illustrated that, feed intake (P ≤ 0.01), weight gain (P ≤ 0.01), FCR (P ≤ 0.05), PER (P ≤ 0.01) and dressing percentages (P ≤ 0.01) were negatively affected by Hyacinth beans inclusion levels (15%, 20%). Neither the processing method practiced for Hyacinth beans nor the enzyme additives were able to improve the performance of broilers better than or comparable to that of basal control broiler diet. The results as well revealed that, treatment diets of 15% Hyacinth beans displayed better performance than 20% level for all of the parameters measured including the dressing percentages and internal organs relative weight.
Keywords: Hyacinth Beans, Processing, Broilers Performance
Previous issue | Next issue | Archive

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|


